【原创】SpringBoot 这几种配置文件方式,你都用过吗?
关注“Java后端技术全栈”**
回复“面试”获取全套大厂面试资料
SpringBoot有这几种操作配置文件方式,你都用过吗?
虽说SpringBoot相对SpringMVC来说,配置文件少了很多。但是在日志开发中,还是存在不少配置项需要配置。
以下几种场景:
自定义配置项
将配置项封装为一个对象
自定义配置文件
每个环境对应一套配置
前期准备,搞一个SpringBoot项目
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 d">
配置文件application.properties(可以是application.yml或者application.yaml)。每个人的喜好不一样。
在配置文件里自定义配置项
myName=zhangsan
package com.example.demo;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class DemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args);
}
}
如何读取自定义配置项
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/properties")
public class TestController {
@Value("${myName}")
private String myName;
@GetMapping("/test")
@ResponseBody
public String test() {
System.out.println(myName);
return myName;
}
}
然后启动项目DemoApplication.java的main方法。
输出
zhangsan
将多个配置项封装为一个对象
通常比如需要把第三方的信息配置到配置文件里。比如说某网站的网址、用户名、密码。
application.properties文件中添加配置项
wangzhan.url=htt://abc.com
wangzhan.userName=root
wangzhan.password=123456
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "wangzhan")
@Component
public class WangzhanConfigBean {
private String url;
private String userName;
private String password;
//get set 省略
}
使用
@RestController()
public class TestController {
@Resource
private WangzhanConfigBean wangzhanConfigBean;
@GetMapping("/test")
public String test() {
String url = wangzhanConfigBean.getUrl();
System.out.println(url);
String userName = wangzhanConfigBean.getUserName();
System.out.println(userName);
String password = wangzhanConfigBean.getPassword();
System.out.println(password);
return "ok";
}
}
输出
htt://abc.com
root
123456
这样我们平时需要自定义配置项的时候,就可以使用上面两种方式解决了。
但是还有一种方式,那就是如果我想自定义配置文件,想在自定义配置文件里进行配置。那又该怎么办呢?
如何读取自定义配置文件内容
比如说,我这里自定义一个配置文件test.properties。
内容
自定义配置文件
user.userName=zhangsan
user.age=22
user.id=1000001
如何读取呢?
@Configuration
@PropertySource(value = "classpath:test.properties")
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "user")
public class UserConfig {
private String userName;
private Integer age;
private Integer id;
//省略 get set
}
使用UserConfig
@RestController()
public class UserController {
@Resource
private UserConfig userConfig;
@GetMapping("/user/{id}")
public String queryUserNameById(@PathVariable("id") Integer id) {
System.out.println(userConfig.getUserName());
return "ok";
}
}
输出
zhangsan
是不是很简单呢?
在工作中,肯定会有开发环境、测试环境、线上环境。这三个还是比较常规的,有的还有灰度环境等。这时候就需要配置多套配置了,那怎么处理起来比较方便呢?
每个环境各自一个配置文件
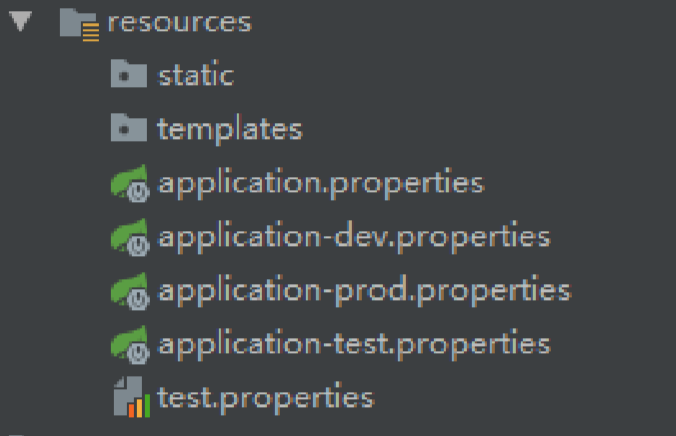
dev端口改成8081
test端口改成8082
prod端口改成8083
现在是开发环境,怎么使用我们配置文件是dev呢?
只需要把application.properties文件清空,然后写入内容
spring.profiles.active=dev
然后启动项目。细心的人会发现,启动日志里会有这么一段日志:
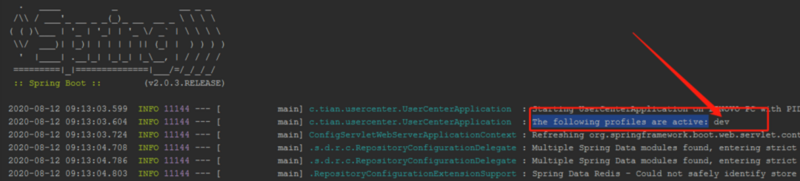
这就是指明了,我们使用的是dev这个配置文件。然后再看看端口是不是我们前面所说的8081
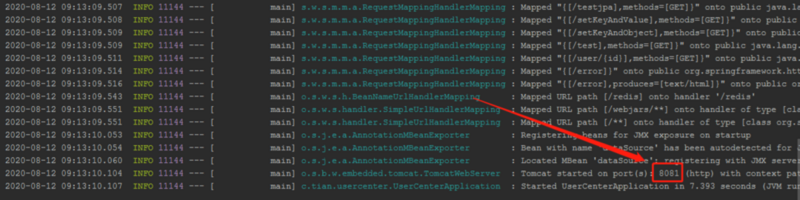
访问一下,前面的自定义配置文件的那个链接
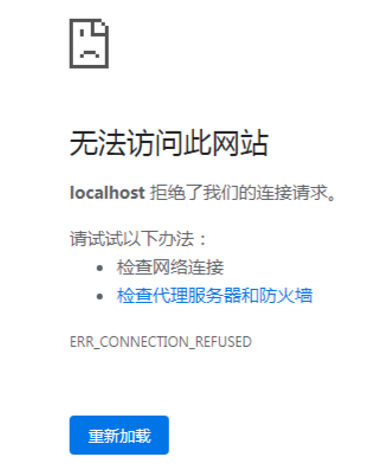
明细之前的8080端口是不能访问了。那么我们换成8081
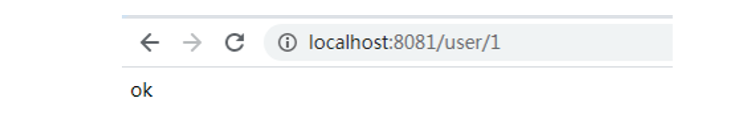
成功。并且输出
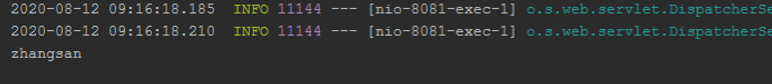
OK。搞定。
推荐阅读
