架构师训练营第7周作业
作业内容
作业1:性能压测的时候,随着并发压力的增加,系统响应时间和吞吐量如何变化,为什么?
系统性能压测一般包括:
我们首先现来看一下
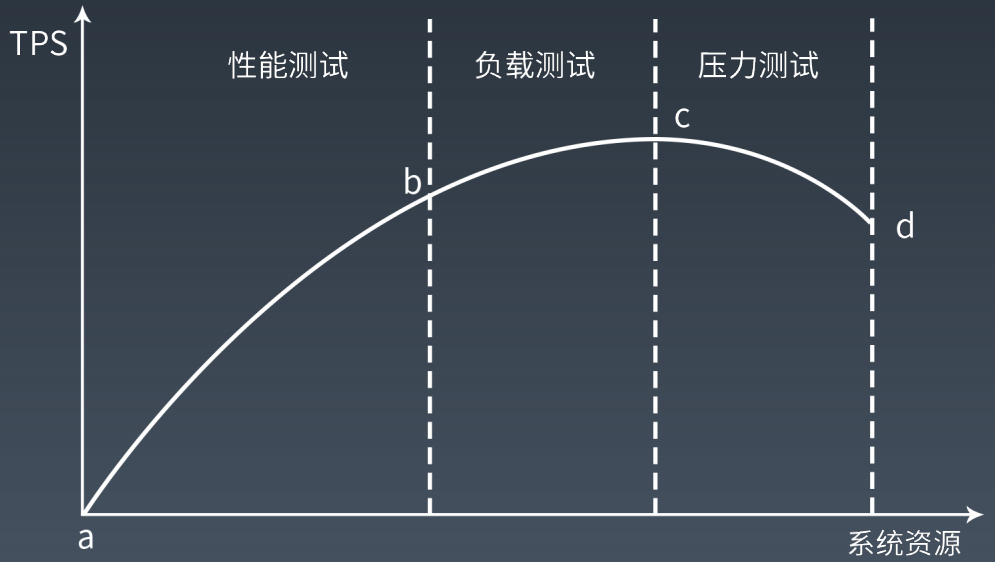
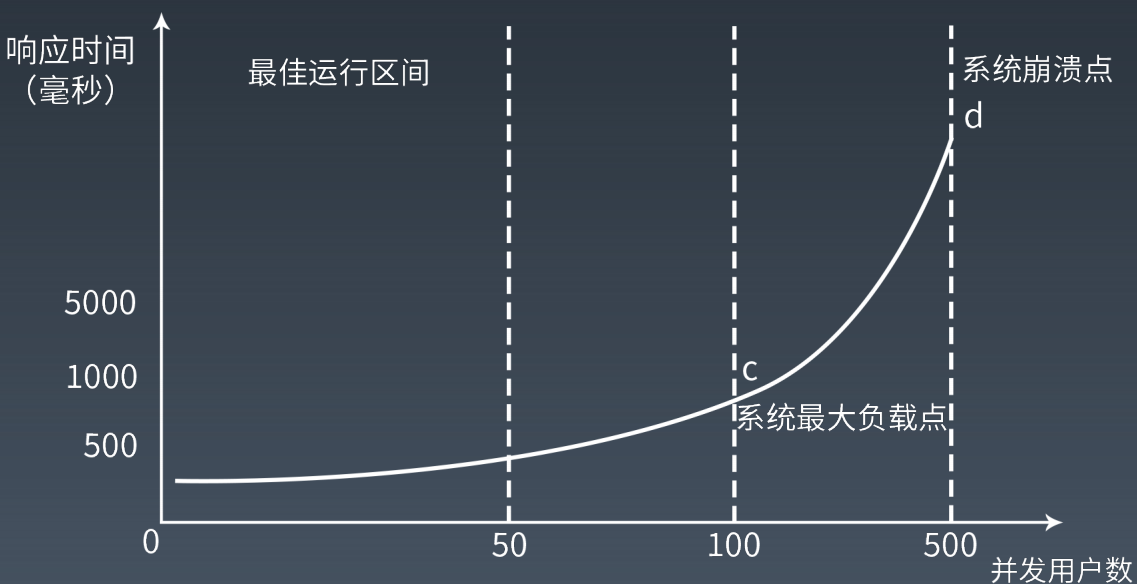
随着并发数的增加,系统运行在性能测试阶段,响应时间会缓慢增加,吞吐量则会快速上升;
当系统的某项或多项性能指标达到安全临界时,如果并发压力继续增加,系统的响应时间增速会加快,吞吐量增速变缓甚至出现下降;
继续增加并发压力,系统进入压力测试阶段,由于超过安全负载,响应时间会极速增加,吞吐量也会快速下降,直至系统崩溃无法提供服务。
上述描述是在正常逐渐增加压力的情况下进行测试,由于真实环境的流量具有不稳定性,为了能够更好地获取系统性能指标,还需要进行
如果不均匀地增加系统并发压力,
下面附上老师课件关于TPS和响应时间随着并发请求增加的情况下的能力变化示意图
作业二:用熟悉的编程语言写一个web性能压测工具
实现思路:
1. 先实现访问url的工具类(我只实现了get方法,返回自定义的HttpResponse对象);
2. 再去写压测实现类,主要方法包括:
a. 带参构造方法,可以指定压测并发数,压测总次数以及压测地址等信息;
b. 获取压测平均响应时间方法;
c. 获取指定%响应时间方法;
d. 打印压测结果方法。
3. 压测测试类
测试输出结果:
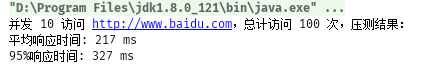
下面是该测试工具的相关源码
/**
* 自定义请求响应类
*/
public class HttpResponse {
// 响应内容
private String content;
// 响应时间
private long respTime;
public String getContent() {
return content;
}
public void setContent(String content) {
this.content = content;
}
public long getRespTime() {
return respTime;
}
public void setRespTime(long respTime) {
this.respTime = respTime;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "HttpResponse{" +
"content='" + content + '\'' +
", respTime='" + respTime +
"ms'}";
}
}/**
* 请求访问工具类
*/
public class HttpClient {
/**
* 获取连接信息
*
* @param url
* @return
*/
private static URLConnection getConnection(String url) {
URLConnection connection = null;
if (Optional.ofNullable(url).isPresent()) {
try {
connection = new URL(url).openConnection();
connection.setRequestProperty("accept", "*/*");
connection.setRequestProperty("connection", "Keep-Alive");
connection.setRequestProperty("user-agent", "Mozilla/4.0 (compatible; MSIE 6.0; Windows NT 5.1;SV1)");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return connection;
}
/**
* GET方式请求简单实现
*
* @param url
* @return
*/
public static HttpResponse get(String url) {
HttpResponse response = new HttpResponse();
StringBuilder content = new StringBuilder();
URLConnection connection = getConnection(url);
try (BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(connection.getInputStream()))) {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
connection.connect();
String line = null;
while ((line = in.readLine()) != null) {
content.append(line);
}
response.setContent(content.toString());
response.setRespTime(System.currentTimeMillis() - start);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return response;
}
}/**
* 压力测试模拟器
*/
public class Simulator {
private String url = null;
private int sbc = 1;
private int times = 1;
/**
* 测试模拟器构造方法
*
* @param url 测试地址
* @param sbc 并发数
* @param times 请求总次数
*/
public Simulator(String url, int sbc, int times) {
this.url = url;
this.sbc = sbc;
this.times = times;
}
/**
* 启动压测
* @return
* @throws InterruptedException
*/
public List start() throws InterruptedException {
List respList = new ArrayList<>();
ThreadPoolExecutor executor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(sbc, sbc,
0L, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingQueue());
for (int i = 0; i < this.times; i++) {
executor.execute(() -> {
HttpResponse resp = HttpClient.get(this.url);
respList.add(resp);
});
}
while (executor.getActiveCount() > 0) {
Thread.sleep(100);
}
executor.shutdown();
return respList;
}
/**
* 获取平均响应时间
*
* @param respList
* @return
*/
public long getAvgRespTime(List respList) {
return Optional.ofNullable(respList).orElse(new ArrayList<>()).stream()
.map(HttpResponse::getRespTime)
.collect(Collectors.averagingLong(Long::longValue)).longValue();
}
/**
* 获取${percent}%响应时间
*
* @param respList
* @return
*/
public long getAvgRespTime(List respList, int percent) {
long avgRespTime = 0L;
Optional> respTimesOptional = Optional.ofNullable(respList);
if (respTimesOptional.isPresent()) {
avgRespTime = respTimesOptional.get().stream()
.map(HttpResponse::getRespTime)
.sorted()
.collect(Collectors.toList())
.get(Math.max(Math.floorDiv(respList.size() * percent, 100) - 1, 0));
}
return avgRespTime;
}
/**
* 打印压测结果
*
* @param respList
*/
public void print(List respList) {
System.out.println(String.format("并发 %d 访问 %s,总计访问 %d 次,压测结果:", this.sbc, this.url, this.times));
System.out.println(String.format("平均响应时间: %d ms", this.getAvgRespTime(respList)));
System.out.println(String.format("95%s响应时间: %d ms", "%", this.getAvgRespTime(respList, 95)));
}
} /**
* 压力测试baidu
*/
public class SimulatorTest {
@Test
public void testSimulator() throws InterruptedException {
String url = "http://www.baidu.com";
int sbc = 10;
int times = 100;
Simulator testSimulator = new Simulator(url, sbc, times);
List respList = testSimulator.start();
testSimulator.print(respList);
}
}