Elasticsearch Fetch Phase
Elasticsearch fetch phase,内容来自 B 站中华石杉 Elasticsearch 顶尖高手系列课程核心知识篇,英文内容来自 Elasticsearch: The Definitive Guide [2.x],内容似乎有些过时,但是我觉得底层原理应该大同小异,欢迎拍砖
Fetch Phase
接着前一篇文章的 Query Phase
一般搜索,如果不加from和size,就默认搜索前10条,按照_score排序
query phase 结束后,coordinate node 获取到的是一堆 doc id 等信息,coordinate node 发送 mget api 去对应的 shard 上,批量一次性获取所需要的数据。
每个 shard 获取了对应的 document 之后,返回给 coordinate node。
coordinate node 拿到所有的 document,返回给 client。
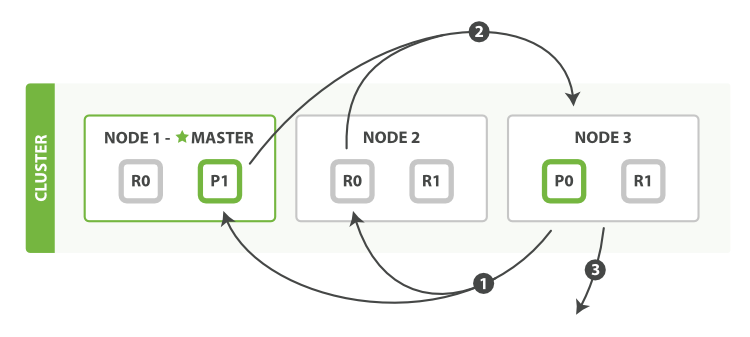
The coordinating node builds a multi-get request for each shard that holds a pertinent document and sends the request to the same shard copy that handled the query phase.
The shard loads the document bodies - the _source field - and, if requested, enriches the results with metadata and search snippet highlighting. Once the coordinating node receives all results, it assembles them into a single response that it returns to the client.
Deep Pagination
deep paging 的问题就是 from + size 分页太深,每个 shard 都要返回大量数据给 coordinate node,消耗大量的带宽、内存和 CPU。
The query-then-fetch process supports pagination with the from and size parameters, but within limits.
Depending on the size fo your documents, the number of shards, and the hardware you are using, paging 10,000 to 50,000 results (1,000 to 5,000 pages) deep should be perfectly doable. But with big-enough from values, the sorting process can become very heavy indeed, using vast amounts of CPU, memory, and bandwidth.
In practice, "deep pagers" are seldom human anyway. A human will stop paging after two or three pages and will change the search criteria. The culprits are usually bots or web spiders that tirelessly keep fetching page after page until your servers crumble at the knees.