【Vuex 源码学习】第七篇 - Vuex 的模块安装
一,前言
上一篇,主要介绍了 Vuex 模块收集的实现,主要涉及以下几个点:
Vuex 模块的概念;
Vuex 模块和命名空间的使用;
Vuex 模块收集的实现-构建“模块树”;
本篇,继续介绍 Vuex 模块相关概念:Vuex 模块安装的实现;
二,前文梳理
Vuex 的根模块,即 index 模块:src/store/index.js:
根模块通过 modules 注册子模块:示例包含 A、B 两个子模块;
模块A 又包含了子模块 C,这样就构建了一个三层的树形结构;
所以,Vuex 的模块,理论上是一棵支持无限层级的模块树;
依赖收集的过程:就是根据 Vuex 模块关系进行数据格式化,体现到代码上就是递归;
通过 类,递归地对 Vuex 模块进行格式化处理,以便于后续的状态操作;
这里,大家可以借鉴组合模式,用于处理树型结构,如组织架构等层级嵌套的场景;
通过 进行模块注册:
数组类型,当前待注册模块的完整路径; 当前待注册模块对象;
至此,在 Vuex 中就完成了模块间层级关系的维护,从而递归构建出一棵“模块树”对象;
备注:
同名模块会在 Vuex 的模块收集阶段被覆盖;
多个模块中存在同名状态时,默认将同时触发更新 ;可添加 namespaced 命名空间进行隔离;
添加了 namespaced 命名空间后,状态操作需添加命名空间标识,如
下一步,根据格式化后的“模块树”对象,实现 Vuex 的模块安装;
三,模块安装的逻辑
模块收集:将模块对象格式化成为一棵“模块树”;
模块安装:递归“模块树”并将所有模块的 getter、mutation、action 定义到当前 store 实例中;
从根模块开始进行模块安装,递归处理格式化后的“模块树”对象;
根据模块名称,将全部子模块定义到根模块上,同时将状态合并到根模块上;
在 Store 类中,创建 installModule 模块安装方法:对当前模块对象进行递归处理;
从根模块开始,将对应的 getter、mutation、action 统一放入 Store 类中的 this._actions、this._mutations、this._wrappedGetters;
备注:由于模块对象不便于能力的扩展,考虑重构为类,将模块相关操作进行封装提供外部调用;
四,代码优化
优化1:将模块对象重构为模块类
创建 Module 类:src/vuex/modules/module.js
// src/vuex/modules/module.js
/**
* Module 模块类,提供模块数据结构与相关能力扩展
*/
class Module {
constructor(newModule) {
this._raw = newModule;
this._children = {};
this.state = newModule.state
}
/**
* 根据模块名获取模块实例
* @param {*} key 模块名
* @returns 模块实例
*/
getChild(key) {
return this._children[key];
}
/**
* 向当前模块实例添加子模块
* @param {*} key 模块名
* @param {*} module 子模块实例
*/
addChild(key, module) {
this._children[key] = module
}
// 基于 Module 类,为模块扩展其他能力...
/**
* 遍历当前模块下的 mutations,具体处理由外部回调实现
* @param {*} fn 返回当前 mutation 和 key,具体处理逻辑由调用方实现
*/
forEachMutation(fn) {
if (this._raw.mutations) {
Object.keys(this._raw.mutations).forEach(key=>fn(this._raw.mutations[key],key));
}
}
/**
* 遍历当前模块下的 actions,具体处理由外部回调实现
* @param {*} fn 返回当前 action 和 key,具体处理逻辑由调用方实现
*/
forEachAction(fn) {
if (this._raw.actions) {
Object.keys(this._raw.actions).forEach(key=>fn(this._raw.actions[key],key));
}
}
/**
* 遍历当前模块下的 getters,具体处理由外部回调实现
* @param {*} fn 返回当前 getter 和 key,具体处理逻辑由调用方实现
*/
forEachGetter(fn) {
if (this._raw.getters) {
Object.keys(this._raw.getters).forEach(key=>fn(this._raw.getters[key],key));
}
}
/**
* 遍历当前模块的子模块,具体处理由外部回调实现
* @param {*} fn 返回当前子模块 和 key,具体处理逻辑由调用方实现
*/
forEachChild(fn) {
Object.keys(this._children).forEach(key=>fn(this._children[key],key));
}
}
export default Module;修改 ModuleCollection 类,将模块对象更新为 Module 类:
import Module from "./module";
class ModuleCollection {
constructor(options) {
this.register([], options);
}
register(path, rootModule) {
// 格式化:构建 Module 对象
// 通过类的方式产生实例,便于后续的扩展
let newModule = new Module(rootModule);
// let newModule = {
// _raw: rootModule, // 当前模块的完整对象
// _children: {}, // 当前模块的子模块
// state: rootModule.state // 当前模块的状态
// }
if (path.length == 0) {
this.root = newModule;
} else {
let parent = path.slice(0, -1).reduce((memo, current) => {
// 此时 memo 为 Module 类,使用 getChild 方法进行处理;
return memo.getChild(current);
// return memo._children[current];
}, this.root)
// 此时 memo 为 Module 类,使用 addChild 方法进行处理;
parent.addChild(path[path.length - 1], newModule);
// parent._children[path[path.length - 1]] = newModule
}
if (rootModule.modules) {
Object.keys(rootModule.modules).forEach(moduleName => {
let module = rootModule.modules[moduleName];
this.register(path.concat(moduleName), module)
});
}
}
}
export default ModuleCollection;优化2:抽取对象遍历工具方法
代码中多次使用 Object.keys 进行对象遍历操作,可封装为工具函数;
创建 src/vuex/utils.js 文件,统一存放 vuex 插件使用的工具函数:
// src/vuex/utils.js
/**
* 对象遍历,返回 value、key,具体处理由外部实现
* @param {*} obj 需要遍历的对象
* @param {*} callback 对当前索引的处理,又外部实现
*/
export const forEachValue = (obj, callback) =>{
Object.keys(obj).forEach(key=>callback(obj[key],key));
}使用工具函数替换 Object.keys:
// src/vuex/module/module-collection.js
import { forEachValue } from "../utils";
import Module from "./module";
class ModuleCollection {
constructor(options) {
this.register([], options);
}
register(path, rootModule) {
let newModule = new Module(rootModule);
if (path.length == 0) {
this.root = newModule;
} else {
let parent = path.slice(0, -1).reduce((memo, current) => {
return memo.getChild(current);
}, this.root)
parent.addChild(path[path.length - 1], newModule);
}
if (rootModule.modules) {
forEachValue(rootModule.modules,(module,moduleName)=>{
this.register(path.concat(moduleName),module)
})
// Object.keys(rootModule.modules).forEach(moduleName => {
// let module = rootModule.modules[moduleName];
// this.register(path.concat(moduleName), module)
// });
}
}
}
export default ModuleCollection;import { forEachValue } from "../utils";
class Module {
constructor(newModule) {
this._raw = newModule;
this._children = {};
this.state = newModule.state
}
getChild(key) {
return this._children[key];
}
addChild(key, module) {
this._children[key] = module
}
forEachMutation(fn) {
if (this._raw.mutations) {
forEachValue(this._raw.mutations, fn)
// Object.keys(this._raw.mutations).forEach(key=>fn(this._raw.mutations[key],key));
}
}
forEachAction(fn) {
if (this._raw.actions) {
forEachValue(this._raw.actions, fn);
// Object.keys(this._raw.actions).forEach(key=>fn(this._raw.actions[key],key));
}
}
forEachGetter(fn) {
if (this._raw.getters) {
forEachValue(this._raw.getters, fn);
// Object.keys(this._raw.getters).forEach(key=>fn(this._raw.getters[key],key));
}
}
forEachChild(fn) {
forEachValue(this._children, fn);
// Object.keys(this._children).forEach(key=>fn(this._children[key],key));
}
}
export default Module;优化后测试
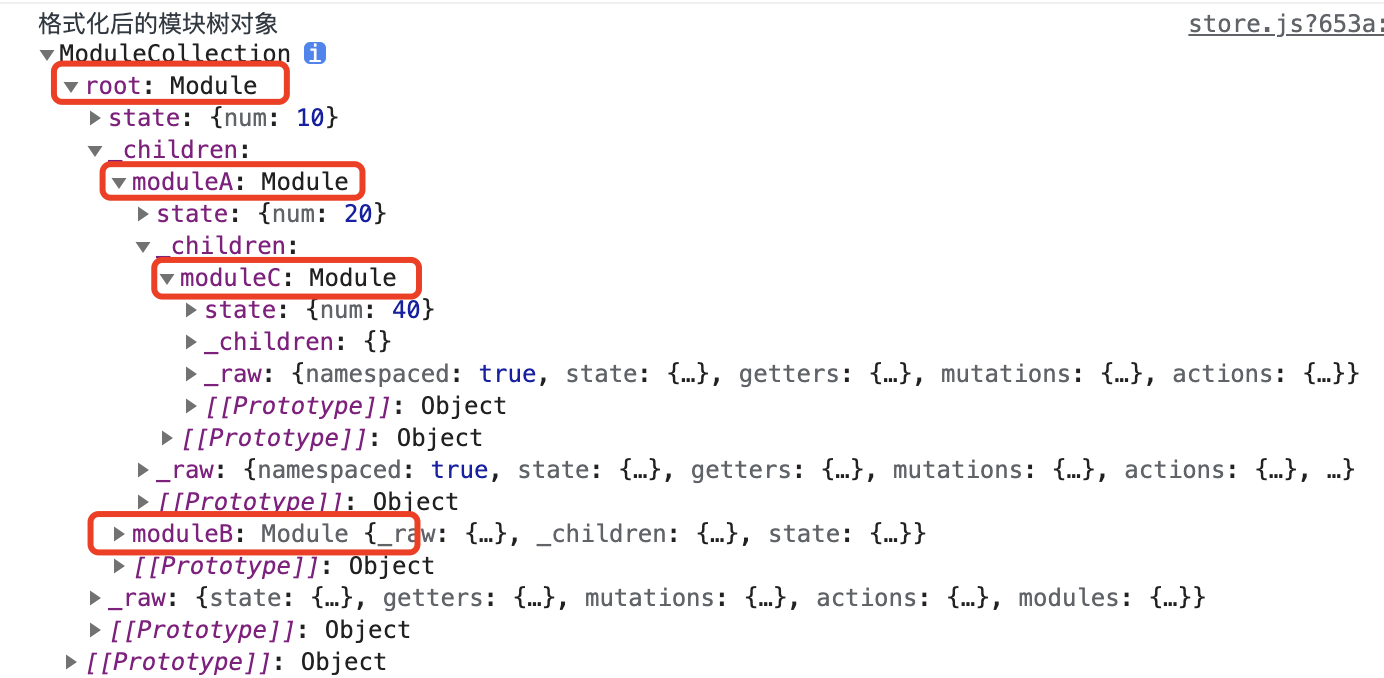
功能正常,模块对象已重构为 Module 类,添加了对当前模块 getters、mutations、actions 的遍历处理;
五,模块安装的实现
在 src/vuex/store.js 中,创建 installModule 方法:用于 Vuex 的模块安装操作;
// src/vuex/store.js
/**
* 安装模块
* @param {*} store 容器
* @param {*} rootState 根状态
* @param {*} path 所有路径
* @param {*} module 格式化后的模块对象
*/
const installModule = (store, rootState, path, module) => {
// 遍历当前模块中的 actions、mutations、getters
// 将它们分别定义到 store 中的 _actions、_mutations、_wrappedGetters;
// 遍历 mutation
module.forEachMutation((mutation, key) => {
// 处理成为数组类型:每个 key 可能会存在多个需要被处理的函数
store._mutations[key] = (store._mutations[key] || []);
// 向 _mutations 对应 key 的数组中,放入对应的处理函数
store._mutations[key].push((payload) => {
// 执行 mutation,传入当前模块的 state 状态
mutation.call(store, module.state, payload);
})
})
// 遍历 action
module.forEachAction((action, key) => {
store._actions[key] = (store._actions[key] || []);
store._actions[key].push((payload) => {
action.call(store, store, payload);
})
})
// 遍历 getter
module.forEachGetter((getter, key) => {
// 注意:getter 重名将会被覆盖
store._wrappedGetters[key] = function () {
// 执行对应的 getter 方法,传入当前模块的 state 状态,返回执行结果
return getter(module.state)
}
})
// 遍历当前模块的儿子
module.forEachChild((child, key) => {
// 递归安装/加载子模块
installModule(store, rootState, path.concat(key), child);
})
}依靠 Module 类提供的模块处理方法,深度递归地将全部模块中的 action、mutation、getter 统一收集到了 store 实例中对应的 _actions、_mutations、_wrappedGetters 中;
模块安装结果测试:
// src/vuex/store.js
// 容器的初始化
export class Store {
constructor(options) {
const state = options.state;
this._actions = {};
this._mutations = {};
this._wrappedGetters = {};
this._modules = new ModuleCollection(options);
installModule(this, state, [], this._modules.root);
console.log("模块安装结果:_mutations", this._mutations)
console.log("模块安装结果:_actions", this._actions)
console.log("模块安装结果:_wrappedGetters", this._wrappedGetters)
}
// ...
}打印 _actions、_mutations、_wrappedGetters 结果:
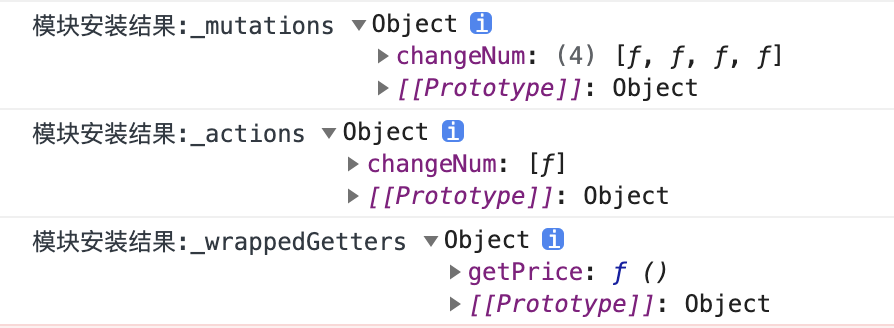
_mutations 共 4 个:根模块、模块 A、模块 B、模块 C;
_actions 共 1 个:根模块;
_wrappedGetters 共 1 个:根模块;
六,流程梳理
当项目引用并注册 vuex 插件时,即 ,将执行 Vuex 插件中的 install 方法;
install 方法,接收外部传入的 Vue 实例,并通过 实现 store 实例的全局共享;
项目中通过 配置 vuex 并完成 store 状态实例的初始化;
在 Store 实例化阶段时,将会对 options 选项进行处理,此时完成 Vuex 模块收集和安装操作;
在 初始化时,将 store 实例注入到 vue 根实例中(此时的 store 实例已实现全局共享);
七,结尾
本篇,主要介绍了 Vuex 模块安装的实现,完成了 action、mutation、getter 的收集和处理,主要涉及以下几个点:
Vuex 模块安装的逻辑;
Vuex 代码优化;
Vuex 模块安装的实现;
Vuex 初始化流程梳理;
下一篇,继续介绍 Vuex 模块相关概念:Vuex 状态的处理;
维护日志
20211006:
重新梳理全文:添加代码优化与流程梳理部分;添加必要的代码注释;添加测试截图;