【Vuex 源码学习】第十二篇 - Vuex 插件机制的实现
一,前言
上一篇,主要介绍了 Vuex 插件的开发,主要涉及以下几个点:
Vuex 插件的使用介绍;
Vuex 插件开发和使用分析;
Vuex 插件机制的分析;
本篇,继续介绍 Vuex 插件机制的实现;
二,Vuex 插件机制分析
通过官方 Vuex 插件所提供的插件机制,创建并实现了一个简易的 Vuex 插件;
Vuex 插件的实现,主要使用 Vuex 提供的以下方法:
Vuex 插件的 plugins 数组,提供插件注册功能;
store.subscribe:状态变更时的订阅回调功能;
store.replaceState:状态替换功能;
本篇继续以 vuex 持久化插件 vuex-persists 为例,逐步实现 Vuex 插件提供的机制核心逻辑;
三,Vuex 插件机制实现
1,Vuex 插件的注册
当 初始化时,处理 options.plugins 数组中注册的插件函数(高阶函数);
收集 Vuex 插件中,通过 store.subscribe 订阅状态变化事件的回调函数 fn 保存到 数组中;
// src/vuex/store.js
export class Store {
constructor(options) {
const state = options.state;
this._actions = {};
this._mutations = {};
this._wrappedGetters = {};
// 收集通过 store.subcribe 订阅状态变更事件的处理函数 fn
// 当 mutation 执行时,触发全部订阅事件执行,返回当前 mutation 和更新后的状态
this._subscribes = [];
this._modules = new ModuleCollection(options);
installModule(this, state, [], this._modules.root);
resetStoreVM(this, state);
// 依次执行 options 选项中的 plugins 插件,传入当前 store 实例
options.plugins.forEach(plugin => plugin(this));
}
// 提供 store.subscribe 状态变更事件订阅功能
// 将回调函数统计收集到 _subscribes 数组中;
subscribe(fn) {
console.log("订阅 Vuex 状态变化,收集处理函数")
this._subscribes.push(fn);
console.log("this._subscribes", this._subscribes)
}
}2,subscribe 状态订阅实现
当状态变化时,即 mutation 方法执行时,依次执行 中保存的处理函数 fn,传入当前 mutation 和当前根状态 rootState;
// src/vuex/store.js
const installModule = (store, rootState, path, module) => {
// ...
module.forEachMutation((mutation, key) => {
store._mutations[namespace + key] = (store._mutations[namespace + key] || []);
store._mutations[namespace + key].push((payload) => {
mutation.call(store, module.state, payload);
// 当 mutation 执行时,依次执行 store.subscribe 状态变更事件订阅的处理函数 fn
store._subscribes.forEach(fn => {
console.log("状态更新,依次执行订阅处理")
fn(mutation, rootState);
})
})
})
// ...
module.forEachChild((child, key) => {
installModule(store, rootState, path.concat(key), child);
})
}
export class Store {
constructor(options) {
const state = options.state;
this._actions = {};
this._mutations = {};
this._wrappedGetters = {};
this._subscribes = [];
this._modules = new ModuleCollection(options);
// 模块安装处理 mutation 时,触发状态变更订阅事件通知
installModule(this, state, [], this._modules.root);
resetStoreVM(this, state);
// 依次执行 options 选项中的 plugins 插件,传入当前 store 实例
options.plugins.forEach(plugin => plugin(this));
}
}测试 Vuex 插件的初始化和状态变化时间订阅:
// src/store/index.js
import Vue from 'vue';
import Vuex from '@/vuex'; // 使用自开发的 Vuex 插件
Vue.use(Vuex);
function persists() {
return function (store) {
console.log("----- persists 插件执行 -----")
store.subscribe((mutation, state) => {
console.log("----- 进入Vuex 插件 store.subscribe 处理函数-----")
localStorage.setItem('VUEX:STATE', JSON.stringify(state));
})
}
}
const store = new Vuex.Store({
plugins: [
persists()
],
});
export default store;在 Vuex 插件初始化过程中 plugins 插件被依次执行,并收集插件中通过 store.subscribe 进行状态变更订阅的回调函数 fn;
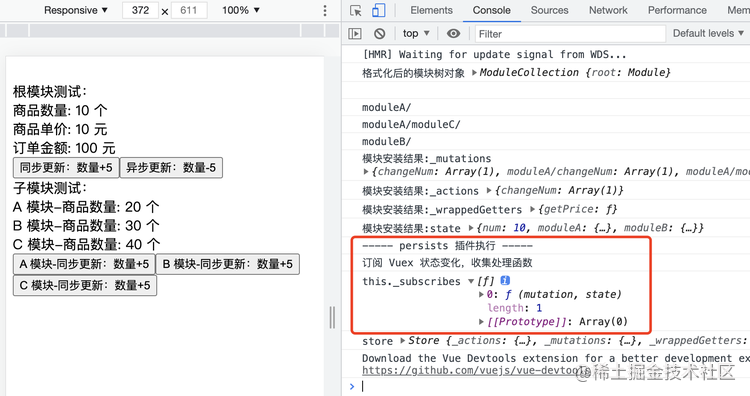
点击按钮更新 Vuex 中的状态,在对应 mutation 方法执行时,依次调用订阅函数,通知 Vuex 插件状态发生变化:
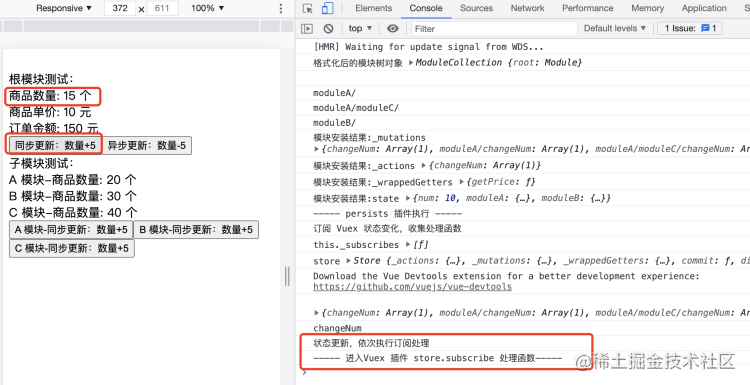
订阅回调中处理:将当前最新的根状态保存至本地存储:
3,replaceState 状态替换实现
当状态更新时,将最新状态保存至本地存储中;
当页面刷新时,读取本地存储并重新设置 Vuex 状态,刷新状态持久化;
插件初始化时,读取本都存储,进行 Vuex 状态同步:
// src/store/index.js
import Vue from 'vue';
import Vuex from '@/vuex';
Vue.use(Vuex);
function persists() {
return function (store) {
console.log("----- persists 插件执行 -----")
// 取出本地存储的状态
let data = localStorage.getItem('VUEX:STATE');
if (data) {
console.log("----- 存在本地状态,同步至 Vuex -----")
// 如果存在,使用本地状态替换 Vuex 中的状态
store.replaceState(JSON.parse(data));
}
store.subscribe((mutation, state) => {
console.log("----- 进入Vuex 插件 store.subscribe 处理函数-----")
localStorage.setItem('VUEX:STATE', JSON.stringify(state));
})
}
}
const store = new Vuex.Store({
plugins: [
persists()
]
});
export default store;添加 replaceState 实现,并更新插件逻辑,统一使用最新状态进行处理:
// src/vuex/store.js
// 通过当前模块路径 path,从最新的根状态上,获取模块的最新状态
function getState(store, path){
return path.reduce((newState,current)=>{
return newState[current];
}, store.state); // replaceState 后的最新状态
}
const installModule = (store, rootState, path, module) => {
let namespace = store._modules.getNamespaced(path);、
if (path.length > 0) {、
let parent = path.slice(0, -1).reduce((memo, current) => {
return memo[current]
}, rootState)
Vue.set(parent, path[path.length - 1], module.state);
}
module.forEachMutation((mutation, key) => {
store._mutations[namespace + key] = (store._mutations[namespace + key] || []);
store._mutations[namespace + key].push((payload) => {
// 旧:执行 mutation,传入当前模块的 state 状态
// mutation.call(store, module.state, payload);
// 新:Vuex 持久化需要使用最新的状态,而 module.state是老状态
// 需要通过当前路径 path,获取到当前最新的状态
mutation.call(store, getState(store,path), payload);
store._subscribes.forEach(fn => {
// 旧逻辑:使用根状态 rootState
// fn(mutation, rootState);
// 新逻辑:使用新状态 store.state
fn(mutation, store.state);
})
})
})
module.forEachAction((action, key) => {
store._actions[namespace + key] = (store._actions[namespace + key] || []);
store._actions[namespace + key].push((payload) => {
action.call(store, store, payload);
})
})
module.forEachGetter((getter, key) => {
store._wrappedGetters[namespace + key] = function () {
// 旧逻辑:执行对应的 getter 方法,传入当前模块的 state 状态,返回执行结果
// return getter(module.state);
// 新逻辑:使用最新的状态进行处理
return getter(getState(store,path));
}
})
module.forEachChild((child, key) => {
installModule(store, rootState, path.concat(key), child);
})
}
function resetStoreVM(store, state) {
const computed = {};
store.getters = {};
forEachValue(store._wrappedGetters, (fn, key) => {
computed[key] = () => {
return fn();
}
Object.defineProperty(store.getters, key, {
get: () => store._vm[key]
});
})
store._vm = new Vue({
data: {
$$state: state
},
computed
});
}
export class Store {
constructor(options) {
const state = options.state;
this._actions = {};
this._mutations = {};
this._wrappedGetters = {};
this._subscribes = [];
this._modules = new ModuleCollection(options);
installModule(this, state, [], this._modules.root);
resetStoreVM(this, state);
options.plugins.forEach(plugin => plugin(this));
}
// Vuex 状态替换
replaceState(state){
this._vm._data.$$state = state
}
}备注:虽然通过 replaceState 实现了 Vuex 插件状态的更新,但此时 Vuex 中的逻辑处理中,依旧使用的是 或 旧状态,需要根据模块路径重新获取对应的新状态进行处理;否则页面不会更新;(涉及 mutation、getter、_subscribes回调传参等相关处理逻辑需更新);
4,插件效果测试
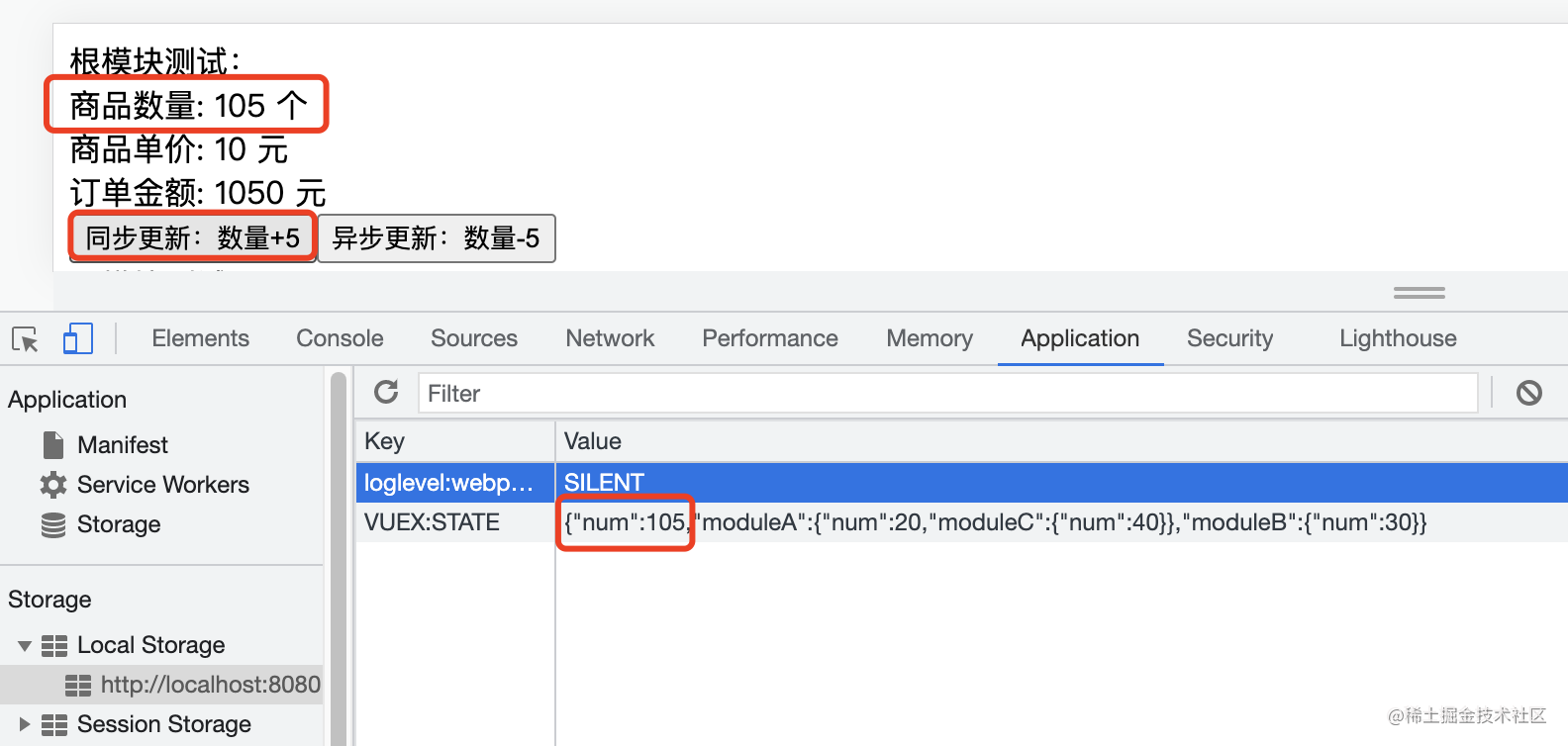
点击按钮更新状态,视图与本地存储同步变化;
页面刷新后,状态持久化成功;
四,结尾
本篇,主要介绍了 Vuex 插件机制的实现,主要涉及以下几个点:
Vuex 插件机制分析;
Vuex 插件机制核心逻辑实现:plugins 插件注册、subscribe 订阅收集、replaceState 状态替换;
下一篇,继续介绍 Vuex 辅助函数的实现;